OptiQ-CanDo: Hybrid Optical Interferometry for Quantitative Cancer Cell Diagnosis
Toward cancer cell diagnosis and grading from a simple blood sample:
Toward cancer cell diagnosis and grading from a simple blood sample:
One of the major challenges in the field of optical imaging of live cells is to achieve label-free but still fully quantitative measurements, which afford high-resolution morphological and mechanical mapping at the single cell level. In particular, developing efficient, non-subjective, quantitative optical imaging technologies for cancer cell diagnosis is a challenging task. In this project, we propose to establish a robust experimental toolbox for label-free optical diagnosis and monitoring of live cancer cells in-vitro and their potential of metastasis. Optical interferometry is able to provide a platform for imaging live cells quantitatively without the risk of effects caused by using external contrast agents. By overcoming critical technological barriers, we suggest novel hybrid optical interferometric approaches that provide a powerful nano-sensing tool for label-free quantitative measurement of cancer cells. This will be obtained by recording the dynamic quantitative, three-dimensional sub-nanometric structural and mechanical characterization of live cancer cells in different stages. For this aim, we will develop a novel low-noise broadband, common-path, off-axis interferometric system for sub-nanometric physical thickness and mechanical mapping of live cells in thousands of frames per second. Additionally, we will develop rapid tomographic approach for fully capturing the cell three-dimensional refractive-index distribution, as a tool to characterize cancer progression. Interferometry will be combined with micro-manipulation of single cells to enable full rotation, imaging of non-adherent cells, and mechanical measurement validation. New set of interferometry-based quantitative parameters will be developed to enable characterization of cellular transformations, and used to characterize cancer cells with different metastasis potential, for cell lines and for circulating tumor cells.
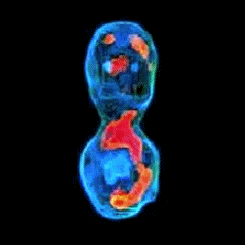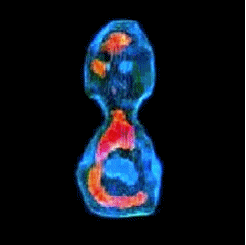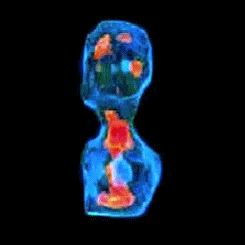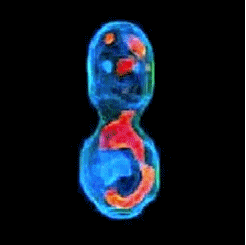
3-D refractive index map of yeast cells obtained by the proposed TPM-HOTs technique.


